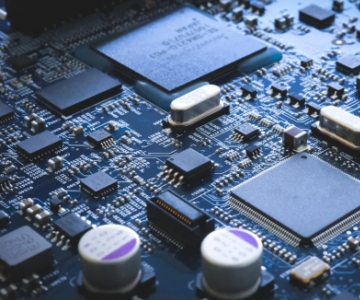
PCB: Components and Their Effects
Generally speaking, PCB itself is made up of several main components. These PCB components include substrate, transistors, resistors, capacitors, etc., which all play their part to ensure we have a smooth-running device -- if one of these components fails, the entire PCB will fail to work and thus affect the functionality of the product itself. In this article, we will outline eleven of the most important and common PCB components and look at why they are so important.
11 Main Components for Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
1. Substrate (FR4)
The substrate is the base material for the PCB, which is usually made up of fire-retardant materials of fiberglass. It is typically known as FR4, with the FR standing for “fire retardant.” It retains its sturdiness and electrical insulating qualities in both humid and dry environments.
2. Resistors
Resistors are one of the most crucial and common components in PCB. They transmit an electric current to produce a voltage and dissipate electric power as heat. They can come in a range of different materials and are color-coded to determine their resistance value.
3. Transistors
The transistor is simply an amplifier used to switch or control the electronic signals in a board. It has several different variations but the most common is the bipolar transistor, which consists of three pins – the base, the collector, and the emitter.
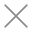
4. Capacitors
Capacitors are the second most common component after resistors. It is to hold an electrical charge within the board and then release it when more power is needed elsewhere in the circuit. Capacitors typically work by collecting opposite charges on two conductive layers that are separated by an insulating material.
5. Inductors
Inductors are similar to capacitors in that they store energy in the form of a magnetic field when current flows through them. They often block signals within the board, such as interference from another electronic device.
6. Transformers
Transformers are commonly used to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another by an increase, or decrease, in voltage.
7. Diodes
The diode is a device in the circuit that allows the electrical current to flow in one direction, but not in the other. This can be used to block current from flowing in the wrong direction, which could damage the board and the device. The most popular form of diode is the LED (Light Emitting Diode).

8. Sensors
These devices are used to detect changes in environmental conditions and generate an electrical signal that corresponds to the change. This signal is then sent to the other components in the circuit board. Sensors convert physical elements like light motion, air quality, or sound into electrical energy like a transducer.
9. Copper Foil
An essential raw material, copper foil, is laminated onto the substrate to create the printed circuit board. The weight of the foil (thickness) ranges from 1⁄4 oz to 2 oz typically. Heavier copper provides better current carrying capacity.
10. Solder Mask
The layer on top of the copper foil is the solder mask layer. It protects the copper from corrosion, which can damage the PCB. The solder mask can be either tin-lead, nickel, gold, or all three of them. Quite often, the solder mask is green in color, which gives the PCB a distinctive look.
11. Silkscreen
The silkscreen layer is applied on top of the solder mask layer. Its purpose is to help us better understand the board by adding symbols, letters, and numbers. The function of every pin and LED is usually indicated. White is most commonly used, but a good contrasting color to the solder mask’s color is generally chosen.

Before moving into final PCB production, it must be verified to ensure that all components are connected and working properly to power the board.